TECH
What Is the Windows Security Button? A Complete Guide for Tablet and PC Users

When using certain Windows tablets and 2-in-1 devices, you may have noticed prompts that say: “Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete or use the Windows Security Button.” For many, this can feel confusing, especially if the device doesn’t have a traditional keyboard. The Windows Security Button exists to replicate the same secure login process as pressing the famous Ctrl+Alt+Delete key combination on a regular computer. It ensures safe authentication and quick access to essential system functions, making it a crucial feature in Microsoft’s security ecosystem.

Understanding the Secure Attention Sequence (SAS)
To grasp why this feature exists, we first need to explore the concept of the Secure Attention Sequence (SAS). Introduced in early versions of Windows, SAS is the technical term for pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
The purpose of this sequence is security. It’s a hardware-level command that cannot be intercepted by malicious software. By requiring users to press it before logging in, Windows ensures the login screen is authentic and not a spoof created by malware. This measure prevents password theft and protects user accounts from unauthorized access.
On desktop PCs with physical keyboards, triggering SAS is simple. But on tablets and devices without a keyboard, Microsoft had to introduce an alternative method—the Windows Security Button.
Why Tablets Need a Security Button
Modern computing devices are becoming slimmer, portable, and often designed without permanent keyboards. Tablets, convertibles, and touch-only laptops make portability easier but complicate traditional security controls.
Without a keyboard, pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete isn’t always possible. To bridge this gap, manufacturers included a dedicated hardware feature or button combination that mimics the Secure Attention Sequence. This replacement makes sure that tablet users enjoy the same protection as desktop users, maintaining consistency across devices.

How the Security Button Works
The security button doesn’t perform any new magic—it simply tells Windows to trigger the same secure action that Ctrl+Alt+Delete would. Once pressed, the device presents the familiar Windows Security screen with options like:
- Lock the computer
- Switch User
- Sign Out
- Change Password
- Open Task Manager
This menu is especially useful in corporate and multi-user environments. For instance, employees can quickly lock their tablet when stepping away, while IT staff can access Task Manager to monitor processes without signing out.
Location and Activation Across Devices
The placement of this button varies depending on the manufacturer.
- Acer tablets often use a special Windows hardware key in combination with the Power button.
- Lenovo ThinkPad and Miix devices typically require pressing the Windows logo key together with the Power button.
- Some Surface models allow users to enable an on-screen equivalent through the ease-of-access settings.
This variability can confuse new users, which is why many system prompts remind you of both options: “Press Ctrl+Alt+Delete or use the Windows Security Button.”
Everyday Scenarios Where It Matters
The importance of this feature goes beyond logging in. Here are practical ways it improves daily computing:
1. Enhanced Security in Public Spaces
If you’re using a tablet in a café or coworking hub, a quick tap of the button lets you lock the screen before walking away. This protects sensitive files from prying eyes.
2. Simplified Multi-User Switching
In households or schools where devices are shared, users can easily switch accounts without restarting. The button provides fast access to the Switch User function.
3. Fast Access to Task Manager
When an application freezes on a tablet without a physical keyboard, opening Task Manager can feel tricky. Using the button provides a straightforward solution without relying on shortcuts.
Windows Security Button vs. Ctrl+Alt+Delete
Both options ultimately serve the same purpose—triggering the Secure Attention Sequence. However, their usage differs depending on the type of device:
| Feature | Ctrl+Alt+Delete | Security Button |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Requires keyboard | Found on tablets/2-in-1 devices |
| Input Method | Three-key press | Physical button or key combo |
| Functions Provided | Lock, Switch User, Task Manager, etc. | Lock, Switch User, Task Manager, etc. |
| Security Level | Hardware-level | Equivalent, hardware-driven |
This shows that the button isn’t a replacement—it’s simply an adaptation for portable form factors.
Troubleshooting: When the Button Doesn’t Work
Some users report situations where pressing the button doesn’t seem to trigger the Windows Security screen. If this happens, try the following:
- Check Device Manuals – Each manufacturer uses different button combinations. Ensure you’re pressing the correct keys.
- Use On-Screen Alternatives – If hardware input fails, use the on-screen keyboard to press Ctrl+Alt+Delete.
- Update System Drivers – Outdated firmware or system drivers may interfere with hardware functions.
- Fallback Options – In corporate environments, IT admins can disable the requirement for SAS, though this is not recommended for personal security.

Best Practices for Secure Usage
- Always lock your screen when stepping away, especially in shared or professional environments.
- Use the button as a quick gateway to Task Manager instead of forcing a reboot when apps freeze.
- If your device lacks the feature, consider enabling on-screen SAS input in Windows accessibility settings.
- Keep your device updated—security patches ensure the SAS system remains reliable.
FAQs
What exactly does the Windows Security Button do?
It triggers the Secure Attention Sequence, which brings up the Windows Security screen with options like Lock, Switch User, Sign Out, Change Password, and Task Manager.
Where is the Windows Security Button located?
Its location depends on the manufacturer. Some tablets use a combination like the Windows key + Power button, while others may have a dedicated physical key.
Is the button available on all devices?
No. Desktops and laptops with physical keyboards usually rely on Ctrl+Alt+Delete. The button is more common on tablets and hybrid devices.
Can I disable the Secure Attention Sequence requirement?
Yes, system administrators can disable the need for SAS before login, but it reduces security and isn’t recommended for personal use.
What happens if the button doesn’t work?
You can use the on-screen keyboard to press Ctrl+Alt+Delete, check for driver updates, or consult your device manual for the correct key combination.
Why does Windows still require Ctrl+Alt+Delete or its equivalent?
Because it’s a secure, hardware-level signal that prevents malware from creating fake login screens to steal passwords.
Conclusion
The Windows Security Button may seem like a mysterious extra feature at first, but its purpose is clear: to provide tablet and hybrid device users with the same protection and convenience as traditional keyboard shortcuts. By replicating the Secure Attention Sequence, it ensures secure logins, quick access to system management tools, and an easy way to lock or switch users.
TECH
Virtualization Technology: The Invisible Engine Powering Modern Computing

Virtualization technology has quietly become the backbone of modern computing, yet most people only notice it when something breaks—or when costs suddenly drop and systems magically scale. I’ve watched this shift firsthand over the last decade. What used to require entire server rooms, weeks of provisioning, and budget approvals now happens in minutes with a few clicks. That change didn’t come from faster hardware alone. It came from virtualization technology fundamentally rewriting how we think about computing resources.
If you’ve ever spun up a cloud server in under five minutes, tested software on multiple operating systems without owning multiple machines, or recovered from a system failure faster than seemed possible, you’ve already benefited from virtualization technology—whether you realized it or not.
This article is for IT professionals, developers, founders, decision-makers, and curious technologists who want more than surface-level definitions. We’ll go deep without getting lost in jargon. You’ll learn how virtualization technology actually works, where it delivers real business value, what tools are worth your time, and what mistakes quietly cost organizations money and performance.
By the end, you’ll understand not just what virtualization technology is, but how to use it intelligently—with the confidence of someone who’s seen both the wins and the pitfalls.
What Is Virtualization Technology? From Simple Concept to Expert-Level Understanding
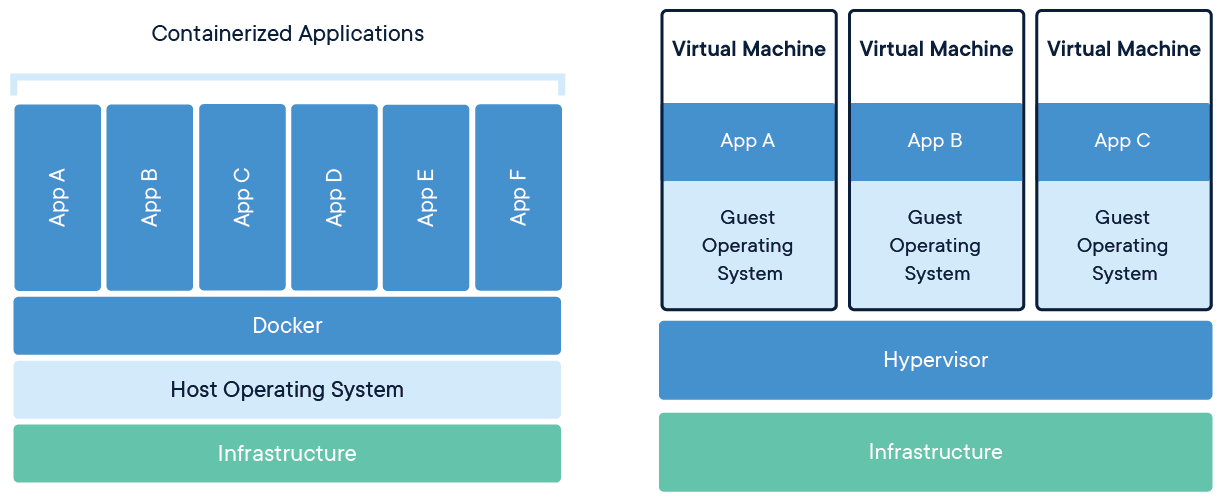
At its core, virtualization technology is about abstraction. It separates physical computing resources—like CPU, memory, storage, and networking—from the systems that use them. Instead of one physical machine running one operating system for one purpose, virtualization technology allows a single machine to behave like many independent machines at once.
A simple analogy I often use is real estate. Imagine owning a large building. Without virtualization, you can only rent the entire building to one tenant. With virtualization technology, you divide that building into apartments, each with its own locks, utilities, and address. Every tenant believes they have their own space, even though they all share the same physical structure.
Technically, this is made possible by a layer called a hypervisor. The hypervisor sits between the hardware and the operating systems, allocating resources dynamically. Each virtual machine (VM) runs its own OS and applications, completely isolated from others—even though they share the same physical hardware.
As you move from beginner to expert understanding, virtualizationtechnology expands into multiple layers:
- Server virtualization (most common and foundational)
- Desktop virtualization (VDI)
- Storage virtualization
- Network virtualization
- Application and container virtualization
What matters is not memorizing categories, but understanding the philosophy: decoupling software from hardware to gain flexibility, efficiency, and resilience.
How Virtualization Technology Actually Works Under the Hood
To truly appreciate virtualization technology, you need a mental model of what’s happening behind the scenes. When a virtual machine boots, it’s not directly talking to your CPU or memory. Instead, the hypervisor intercepts those requests and translates them into safe, controlled interactions with the physical hardware.
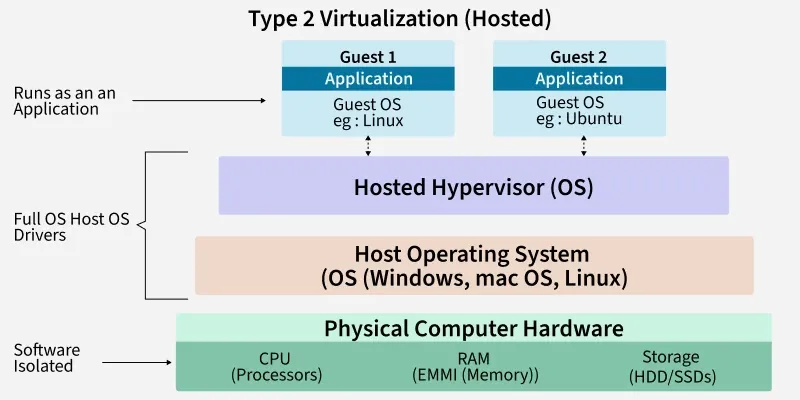
There are two main hypervisor models:
Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the hardware. These are used in production data centers because they offer better performance and security. Type 2 hypervisors run on top of an existing operating system and are commonly used for development, testing, and learning.
The hypervisor manages:
- CPU scheduling (who gets processing time and when)
- Memory allocation and isolation
- Virtual disk mapping to physical storage
- Virtual networking between machines
What’s remarkable is how invisible this process becomes. A virtual machine believes it owns the hardware. Applications behave normally. Yet everything is abstracted, monitored, and controlled.
This abstraction is what enables features like live migration—moving a running VM from one physical server to another with zero downtime. Ten years ago, that sounded like science fiction. Today, it’s routine.
Why Virtualization Technology Became Non-Negotiable in Modern IT
There was a time when virtualization technology was considered optional—an optimization, not a necessity. That era is gone. Today, organizations that avoid virtualization struggle to compete on cost, speed, and reliability.
From my experience, the biggest driver isn’t performance—it’s agility. Virtualization technology allows teams to respond to change without waiting on hardware. New project? Spin up a VM. Traffic spike? Allocate more resources. Hardware failure? Migrate workloads automatically.
The financial impact is equally significant. Before virtualization, servers typically ran at 10–15% utilization. The rest of the capacity sat idle, burning electricity and budget. Virtualization pushed utilization into the 60–80% range, dramatically improving ROI.
It also changed how we think about risk. Instead of “this server can’t fail,” the mindset became “failure is expected, and we design around it.” Virtualization technology made resilience affordable.
Real-World Benefits and Use Cases of Virtualization Technology
The true value of virtualization technology shows up in practical, everyday scenarios—not marketing slides. Let’s look at where it consistently delivers results.
In enterprise IT, virtualization technology consolidates hundreds of physical servers into a manageable virtual environment. This reduces hardware costs, simplifies management, and improves disaster recovery. I’ve seen organizations cut data center footprints in half while improving uptime.
In software development, virtualization technology enables realistic testing environments. Developers can replicate production systems, test multiple OS versions, and isolate experiments without fear of breaking their main machine.
For startups and small businesses, virtualization technology levels the playing field. You no longer need enterprise-grade budgets to run scalable infrastructure. Virtual machines and containers provide flexibility that was once exclusive to large corporations.
Education, healthcare, finance, and government all rely heavily on virtualization technology for security and compliance. Isolated environments make it easier to enforce policies and reduce blast radius when incidents occur.
The “before vs after” difference is striking. Before virtualization: rigid infrastructure, long provisioning times, high costs. After virtualization: flexible systems, rapid deployment, predictable scaling.
A Step-by-Step Practical Guide to Implementing Virtualization Technology
Implementing virtualization technology doesn’t start with software—it starts with clarity. The biggest mistakes I’ve seen happen when teams virtualize without a clear objective.
First, define your goal. Are you consolidating servers, improving disaster recovery, supporting development, or enabling cloud migration? Each goal influences your design choices.
Second, assess your hardware. Virtualization thrives on CPU cores, RAM, and fast storage. Underpowered hardware leads to poor experiences and unfair blame on the technology.
Third, choose the right hypervisor. Enterprise environments often use platforms like VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V. Open-source options like KVM are excellent for cost-conscious teams with Linux expertise.
Fourth, design your virtual networking and storage carefully. This is where performance and security are won or lost. Separate workloads, plan for growth, and avoid shortcuts that create technical debt.
Finally, implement monitoring and backups from day one. Virtualization technology amplifies both good and bad practices. Visibility and recovery planning are not optional.
Containers vs Virtual Machines: Where Virtualization Technology Is Headed
No discussion of virtualization technology is complete without addressing containers. While virtual machines virtualize hardware, containers virtualize the operating system. They’re lighter, faster, and ideal for modern application architectures.
Tools like Docker and orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes have changed how applications are built and deployed. Containers start in seconds, scale effortlessly, and fit perfectly with DevOps workflows.
That said, containers don’t replace virtual machines—they complement them. In practice, containers often run inside virtual machines. VMs provide isolation and security boundaries; containers provide speed and efficiency.
Understanding when to use each is a mark of real expertise in virtualization technology.


Tools, Platforms, and Expert Recommendations
Choosing virtualization technology tools is less about “best” and more about “best fit.” VMware remains a gold standard for enterprise environments, offering mature features and strong ecosystem support. The trade-off is cost.
Hyper-V integrates well with Windows-centric environments and offers solid performance at a lower price point. KVM shines in Linux-heavy infrastructures and cloud platforms.
For desktop virtualization, VDI solutions enable secure remote work but require careful sizing to avoid performance complaints.
My expert advice: start simple, prove value, and scale deliberately. Over-engineering early is a common—and expensive—mistake.
Common Virtualization Technology Mistakes (And How to Fix Them)
The most common mistake is overcommitting resources without monitoring. Virtualization makes it easy to allocate more than you physically have. Without visibility, performance degrades silently.
Another frequent error is treating virtual machines like physical servers. VMs should be disposable, standardized, and automated—not lovingly hand-crafted snowflakes.
Security misconfigurations are also widespread. Isolation is powerful, but only when networks, permissions, and updates are properly managed.
The fix is discipline: monitoring, documentation, and automation. Virtualization technology rewards teams who treat infrastructure as a system, not a collection of machines.
The Future of Virtualization Technology
Virtualization technology continues to evolve alongside cloud computing, edge computing, and AI workloads. We’re seeing deeper integration with automation, policy-driven management, and hardware acceleration.
What won’t change is the core idea: abstraction creates flexibility. As long as computing demands keep changing, virtualization technology will remain essential.

Conclusion: Why Mastering Virtualization Technology Is a Career and Business Advantage
Virtualization technology isn’t just an IT skill—it’s a strategic advantage. It empowers organizations to move faster, spend smarter, and recover stronger. For individuals, understanding it opens doors across cloud, DevOps, security, and infrastructure roles.
If you take one thing away from this guide, let it be this: virtualization technology is not about servers—it’s about choices. The ability to adapt, scale, and innovate without being constrained by hardware is what defines modern computing success.
Start small. Experiment. Learn deeply. And let virtualization technology work for you, not against you.
FAQs
What is virtualization technology in simple terms?
It’s a way to run multiple virtual systems on one physical machine by abstracting hardware resources.
Is virtualization technology the same as cloud computing?
No, but cloud computing relies heavily on virtualization technology to deliver scalable resources.
Does virtualization reduce performance?
There is minimal overhead with modern hypervisors, often outweighed by efficiency gains.
Are containers a replacement for virtual machines?
No. Containers and virtual machines serve different but complementary purposes.
Is virtualization technology secure?
When configured correctly, it improves security through isolation and controlled access.
TECH
DXL Technology: The Practical Guide to Building Smarter, Faster, Experience-Driven Systems

If you’ve ever sat in a meeting where everyone agrees “our systems don’t talk to each other”—you already understand why DXL technology matters.
Most organizations today aren’t short on software. They’re drowning in it. CRMs, ERPs, analytics tools, marketing platforms, identity systems—each powerful on its own, but painfully disconnected when real users expect seamless, instant experiences.
DXL technology exists to solve that exact problem.
This guide is written for architects, product leaders, developers, and decision-makers who are tired of patchwork integrations and brittle APIs. Whether you’re just hearing the term for the first time or you’re evaluating how to operationalize it at scale, this article will give you a clear mental model, real-world use cases, practical implementation steps, and expert-level insights you won’t find in shallow explainers.
By the end, you’ll know:
- What DXL technology really is (and what it isn’t)
- Why it’s becoming foundational to modern digital systems
- How to implement it without over-engineering
- Where teams go wrong—and how to avoid those traps
What Is DXL Technology? (Explained Without the Buzzwords)

DXL technology—short for Digital Experience Layer technology—is an architectural approach designed to sit between backend systems and front-end experiences.
Think of it as a translator and orchestrator.
Instead of forcing every application (web, mobile, kiosk, partner API, internal tool) to talk directly to dozens of backend systems, DXL technology creates a centralized experience layer that:
- Aggregates data from multiple sources
- Applies business logic
- Enforces security and permissions
- Delivers clean, context-aware responses tailored to each experience
A useful analogy is a restaurant kitchen.
Without DXL technology, every customer walks into the kitchen and tries to cook their own meal—grabbing ingredients from wherever they can find them. Chaos follows.
With DXL technology, the kitchen stays hidden. Customers interact with a menu. Orders are coordinated, optimized, and delivered consistently—regardless of how complex the kitchen actually is.
At a technical level, DXL technology often includes:
- API orchestration
- Data normalization
- Experience-specific endpoints
- Event-driven messaging
- Caching and performance optimization
But the real value isn’t technical elegance. It’s experience reliability at scale.
Why DXL Technology Matters More Now Than Ever
DXL technology isn’t a trend—it’s a response to how modern systems actually behave in the real world.
A decade ago, most organizations supported:
- One website
- One mobile app
- A handful of internal tools
Today, the same organization might support:
- Multiple web experiences
- iOS and Android apps
- Partner portals
- Embedded widgets
- Headless CMS outputs
- Voice interfaces
- AI-driven personalization layers
Each of those experiences expects fast, contextual, reliable data.
Without DXL technology, teams usually fall into one of two traps:
- Frontend overload – business logic leaks into apps, creating duplication and bugs
- Backend sprawl – every new channel requires custom integrations
DXL technology creates a stable middle layer that absorbs change without breaking experiences.
From an SEO and performance perspective, this matters because:
- Faster APIs mean better Core Web Vitals
- Cleaner data improves personalization signals
- Consistent responses reduce UX friction
- Scalability protects against traffic spikes
In short: DXL technology is how modern digital experiences stay sane.
Benefits of DXL Technology in Real-World Scenarios



The best way to understand DXL technology is to see what changes before and after it’s implemented.
Before DXL Technology
- Each frontend calls multiple backend APIs
- Performance degrades as systems scale
- Minor backend changes break live experiences
- Security rules are duplicated inconsistently
- Development velocity slows over time
After DXL Technology
- Frontends call one optimized experience layer
- Backend changes are abstracted away
- Responses are tailored to device and context
- Security is centralized and enforceable
- Teams ship faster with fewer regressions
Industries seeing the strongest ROI include:
- Financial services (real-time account views)
- Healthcare (unified patient data)
- E-commerce (personalized product experiences)
- SaaS platforms (multi-tenant dashboards)
- Media (content aggregation across channels)
The common thread? Complex data, high expectations, zero tolerance for friction.
How DXL Technology Works in Practice (Step-by-Step)


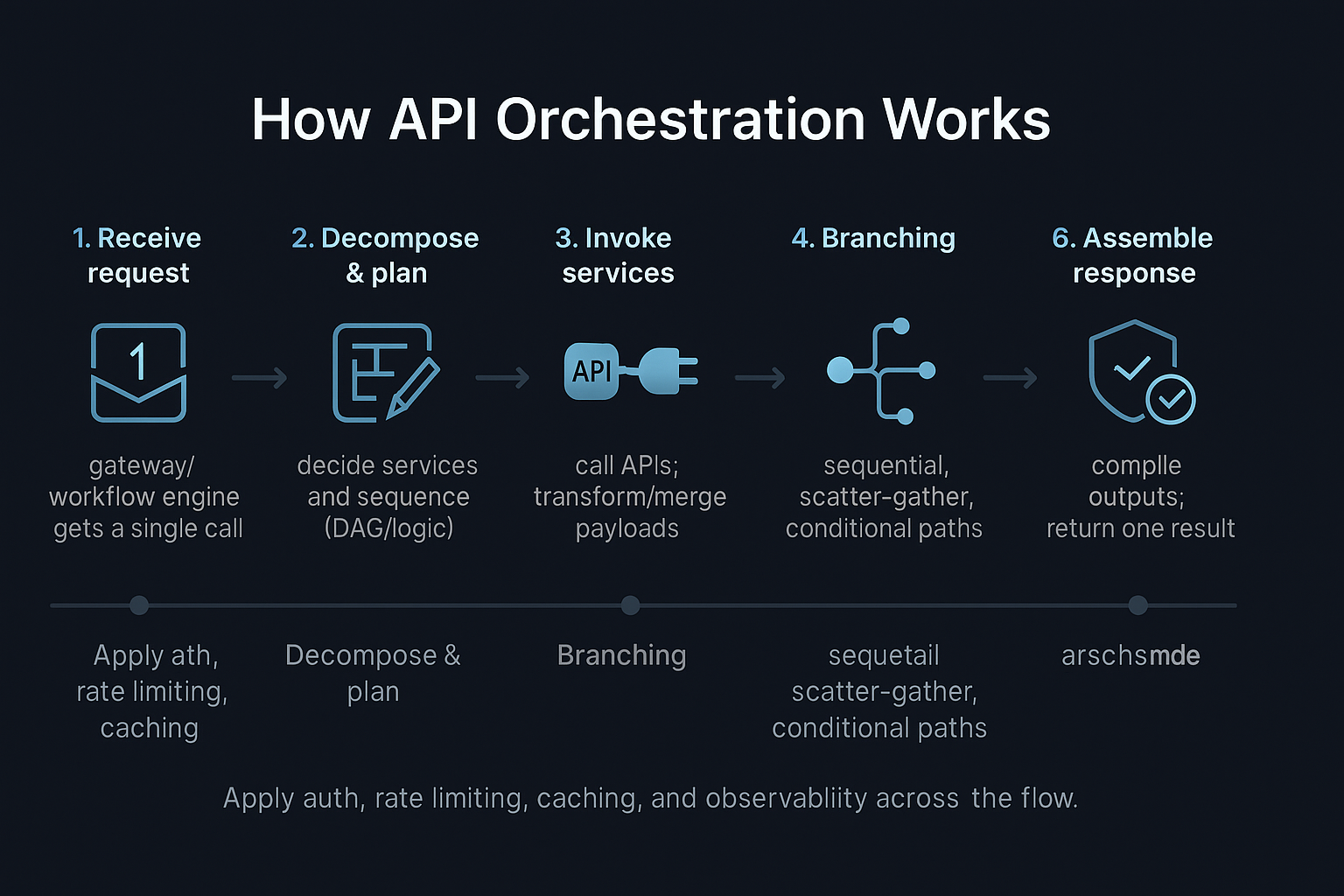
Implementing DXL technology doesn’t mean ripping out your existing stack. Done correctly, it’s additive, not destructive.
Step 1: Map Experience Requirements (Not Systems)
Start with user journeys—not databases.
Ask:
- What does this experience need right now?
- What data must be combined?
- What latency is acceptable?
This prevents over-engineering and keeps DXL technology aligned with business value.
Step 2: Identify Backend Sources of Truth
DXL technology doesn’t replace systems of record. It coordinates them.
Common sources include:
- CRM platforms
- ERP systems
- Identity providers
- Analytics tools
- Content repositories
Each source stays independent. DXL becomes the conductor.
Step 3: Design Experience-Specific APIs
Avoid generic “one-size-fits-all” endpoints.
Instead:
- Create APIs optimized for specific experiences
- Normalize responses
- Remove unnecessary fields
- Apply business rules centrally
This is where performance gains happen.
Step 4: Add Caching, Events, and Resilience
Production-grade DXLtechnology includes:
- Intelligent caching strategies
- Event-driven updates
- Circuit breakers for failing systems
- Graceful degradation paths
This is what separates prototypes from platforms.
Step 5: Monitor and Iterate
DXLtechnology evolves with your experiences.
Track:
- Response times
- Error rates
- Usage patterns
- Downstream dependencies
Optimization is continuous—not a one-time setup.
Tools, Platforms, and Expert Recommendations
There’s no single “DXL technology tool.” Instead, it’s an architectural pattern implemented with different stacks.
Lightweight Approaches
Best for startups and MVPs:
- API gateways with orchestration
- Serverless functions
- GraphQL experience layers
Pros:
- Fast to implement
- Lower cost
- Flexible
Cons:
- Requires discipline to avoid sprawl
Enterprise-Grade Implementations
Best for scale and governance:
- Dedicated experience layer platforms
- Event streaming backbones
- Centralized identity enforcement
Pros:
- Strong security and observability
- Clear ownership models
Cons:
- Higher upfront complexity
Expert Recommendation
Start small.
Build DXLtechnology for one critical journey, prove the value, then expand. Most failures happen when teams try to abstract everything at once.
Common DXL Technology Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
DXLtechnology fails when it becomes theoretical instead of practical.
Mistake 1: Treating DXL as Just Another API Layer
Fix: Design for experiences, not reuse.
Mistake 2: Over-Abstracting Backend Logic
Fix: Keep business rules understandable and documented.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Ownership
Fix: Assign clear responsibility for the experience layer.
Mistake 4: Forgetting Performance Budgets
Fix: Measure, cache, and optimize continuously.
Mistake 5: Building Too Much, Too Soon
Fix: Let real usage drive expansion.
What most teams miss is that DXLtechnology is as much organizational as it is technical.
The Future of DXL Technology
DXLtechnology is increasingly intersecting with:
- AI-driven personalization
- Real-time analytics
- Edge computing
- Headless CMS architectures
As experiences become more dynamic, the experience layer becomes the intelligence hub—not just a data pipe.
Expect future DXL implementations to:
- Adapt responses using AI
- Optimize content per user context
- Orchestrate workflows, not just data
Conclusion: Why DXL Technology Is a Long-Term Advantage
DXLtechnology isn’t about elegance for its own sake.
It’s about:
- Shipping faster without breaking things
- Delivering consistent experiences across channels
- Scaling complexity without losing control
Organizations that invest in DXLtechnology early don’t just move faster—they stay flexible when everything changes.
If you’re serious about modern digital experiences, this is no longer optional.
FAQs
What does DXL technology stand for?
DXL technology refers to Digital Experience Layer technology, an architectural approach for experience-driven systems.
Is DXL technology the same as an API gateway?
No. An API gateway is often a component, but DXLtechnology includes orchestration, logic, and experience optimization.
Who should own DXL technology?
Typically a platform or digital experience team with cross-functional visibility.
Is DXLtechnology only for large enterprises?
No. Smaller teams benefit even more by avoiding future complexity.
Does DXLtechnology improve performance?
Yes—when designed correctly, it reduces redundant calls and optimizes responses.
TECH
15 AI Tools That Actually Matter in 2026 (A Real-World, No-Fluff Guide)

If you’ve searched 15 ai recently, chances are you weren’t looking for another shallow “top tools” list written by someone who hasn’t actually used any of them.
You’re probably here because:
- You keep hearing “AI will replace your job” — but no one explains how to use it properly
- You’ve tested a few tools, felt underwhelmed, and wondered what you’re missing
- Or you’re tired of chasing hype and want practical AI that delivers real results
This guide is written for that exact moment.
I’ve spent years working with content systems, automation workflows, creative tools, and business software. I’ve watched AI evolve from clunky experiments into tools that quietly reshape how work actually gets done. Some of these tools save minutes. Others save entire departments.
This article breaks down 15 AI tools that genuinely matter, not because they’re trendy — but because they solve real problems:
- Creating content faster without sounding robotic
- Automating boring work without breaking systems
- Making smarter decisions with better data
- Turning solo creators into small teams
By the end, you’ll know which AI tools are worth your time, which ones to skip, and how to actually use them without drowning in complexity.
Understanding “15 AI”: What This Phrase Really Means Today
The phrase 15 ai isn’t about a random number. It reflects a deeper shift in how people approach artificial intelligence now.
A few years ago, AI meant one big platform. Today, it means assembling a smart stack — a handful of tools that quietly work together across writing, design, video, research, automation, and decision-making.
Think of AI less like a single machine and more like:
- A set of specialized coworkers
- Each excellent at one task
- None perfect alone
- Extremely powerful together
Beginners often ask, “Which AI should I use?”
Experienced users ask, “Which 10–15 tools cover 80% of my work?”
That’s the mindset behind this list.
I’ve selected these tools based on:
- Real-world usage (not feature lists)
- Consistency over time
- Quality of output
- Learning curve vs payoff
- Long-term relevance (not fads)
This guide moves from creative work → productivity → automation → intelligence, gradually increasing in depth so beginners aren’t overwhelmed — but experienced users still walk away with insights.
Why These 15 AI Tools Are Changing How Work Gets Done
Before diving into individual tools, it’s worth understanding why this specific category of AI tools is exploding.
Most people don’t lack ideas. They lack:
- Time
- Focus
- Consistency
- Energy for repetitive tasks
AI excels exactly where humans burn out.
Here’s what happens before and after adopting the right AI stack:
Before
- Writing takes hours
- Design feels intimidating
- Research is scattered
- Admin work steals creative time
- Output depends on motivation
After
- First drafts appear in minutes
- Design becomes drag-and-drop
- Research is summarized instantly
- Systems run in the background
- Momentum replaces motivation
The real value of these 15 AI tools isn’t “automation.”
It’s mental bandwidth.
When boring work disappears, creative thinking improves — and that’s where real leverage lives.
The 15 AI Tools That Actually Deliver (With Real Use Cases)
1. ChatGPT – Your Thinking Partner, Not Just a Chatbot
Most people use this tool wrong.
They treat it like Google, ask shallow questions, get shallow answers, and declare AI “overrated.” Used properly, it becomes a second brain.
I use it for:
- Outlining complex articles
- Stress-testing ideas
- Turning messy notes into structure
- Role-playing user objections
- Debugging workflows conceptually
The real skill isn’t prompts — it’s context. The more clearly you explain your goal, the better it performs.
Best for: writers, strategists, founders, students
Limitations: needs human judgment, not a final authority
2. Claude – Long-Form Clarity and Reasoning
Where some tools feel punchy and creative, this one feels calm and analytical.
It shines when:
- Handling long documents
- Reviewing contracts or policies
- Maintaining tone across thousands of words
- Explaining complex logic step-by-step
If ChatGPT feels like brainstorming with a fast talker, this feels like sitting with a thoughtful editor.
Best for: long-form writers, analysts, compliance teams
Limitation: less “flash,” more depth
3. Perplexity – Research Without the Rabbit Holes
This tool quietly replaced traditional search for many professionals I know.
Instead of:
- Opening 12 tabs
- Skimming half-relevant articles
- Forgetting sources
You get:
- Clear summaries
- Linked citations
- Follow-up questions that actually make sense
It’s not about speed — it’s about focus.
Best for: journalists, researchers, SEO strategists
Limitation: still depends on source quality
4. Notion AI – Turning Chaos Into Systems
Notion alone is flexible. Add AI, and it becomes adaptive.
I’ve used it to:
- Turn meeting notes into action items
- Summarize weeks of research
- Rewrite SOPs for clarity
- Maintain internal knowledge bases
It’s most powerful when embedded in workflows, not used as a standalone AI toy.
Best for: teams, founders, operations
Limitation: learning curve for new users
5. Grammarly – Polishing Without Killing Your Voice
This tool succeeds because it stays in its lane.
It doesn’t try to write for you.
It helps you sound like your best self.
I trust it for:
- Grammar
- Tone consistency
- Clarity improvements
- Professional communication
Best for: emails, articles, client communication
Limitation: not a creative generator
6. Jasper – Marketing Copy at Scale
This tool is designed for one thing: conversion-focused content.
It performs best when:
- You already know your audience
- You understand messaging
- You need volume without chaos
Used blindly, it sounds generic. Used strategically, it accelerates campaigns.
Best for: marketing teams, agencies
Limitation: requires strong brand guidance
7. Canva – Design Without Design Anxiety
Canva removed the fear from design. AI removed the friction.
I’ve seen non-designers:
- Create pitch decks
- Design social campaigns
- Produce lead magnets
- Maintain brand consistency
It doesn’t replace professional designers — it empowers everyone else.
Best for: creators, small businesses
Limitation: advanced custom design still limited
8. Midjourney – When Visuals Actually Matter
This tool isn’t for quick thumbnails.
It’s for visual storytelling.
Used well, it:
- Creates mood
- Establishes brand identity
- Replaces generic stock imagery
It rewards experimentation and artistic direction.
Best for: brands, artists, storytellers
Limitation: steep learning curve
9. DALL·E – Concept Visualization Made Simple
This shines when you need:
- Quick visuals
- Concept mockups
- Supporting illustrations
It’s faster and more approachable than advanced art tools.
Best for: presentations, ideation
Limitation: less stylistic depth
10. Pictory – Turning Text Into Video Assets
If video feels overwhelming, this tool lowers the barrier.
I’ve used it to:
- Repurpose blog posts
- Create explainer videos
- Produce social clips without cameras
Best for: content marketers
Limitation: template-driven visuals
11. Synthesia – Professional Video Without a Studio
This tool is practical, not flashy.
It’s excellent for:
- Training videos
- Internal communication
- Product walkthroughs
Best for: companies, educators
Limitation: limited emotional range
12. Runway – AI-Assisted Creative Control
Runway sits between creativity and automation.
I’ve seen it:
- Remove backgrounds
- Generate video effects
- Speed up post-production
Best for: video creators
Limitation: requires creative judgment
13. Descript – Editing by Editing Text
This tool changes how you think about audio and video.
Edit words — not waveforms.
Best for: podcasters, YouTubers
Limitation: less granular control
14. Zapier – Quietly Running Your Business
This isn’t glamorous AI — it’s essential AI.
I’ve automated:
- Lead capture
- Email follow-ups
- File organization
- Task creation
Best for: anyone scaling processes
Limitation: setup requires thinking ahead
15. GitHub Copilot – Coding With Momentum
This tool doesn’t replace developers.
It removes friction.
It helps with:
- Boilerplate code
- Debugging suggestions
- Faster iteration
Best for: developers, technical founders
Limitation: not a substitute for understanding code
How to Build Your Own 15 AI Stack (Step-by-Step)
Start with problems, not tools.
- Identify your biggest time drains
- Choose one AI per category
- Master before adding
- Document workflows
- Review monthly
The goal isn’t quantity — it’s coherence.
Common Mistakes People Make With AI (And How to Avoid Them)
- Tool hopping without mastery
- Expecting perfect output instantly
- Automating broken processes
- Ignoring human oversight
AI amplifies systems — good or bad.
FAQs
Is using 15 AI tools too many?
Not if each serves a clear purpose.
Do I need to be technical?
No. Most tools are designed for non-technical users.
Will AI replace my job?
People using AI will replace people who don’t.
Are free tools enough?
For beginners, yes. Professionals usually upgrade.
How long to see results?
Days for productivity, months for mastery.
-

 TECH6 months ago
TECH6 months agoGlow and Type: Exploring Light-Up Computer Keyboards
-

 EDUCATION6 months ago
EDUCATION6 months agoHow Many Teeth Does a Shark Really Have?
-

 BUSINESS6 months ago
BUSINESS6 months agoChoosing the Perfect Salmon Fishing Pole
-

 BUSINESS6 months ago
BUSINESS6 months ago2025 Toyota Fortuner: The Ultimate Blend of Power and Luxury
-

 BLOG6 months ago
BLOG6 months agoAre Gingers Considered Black? Unpacking the Myths and Facts
-

 FOOD6 months ago
FOOD6 months agoLiquid Gold: The Science and Soul of Cooking Oil
-

 FOOD6 months ago
FOOD6 months agoYellowtail Unveiled: The Golden Jewel of the Sea
-

 TECH6 months ago
TECH6 months agoUnveiling the Magic: Why 1 Hacker Way Menlo Park is a Game-Changer
